Atelocollagen Application in Human Periodontal Tissue Treatment
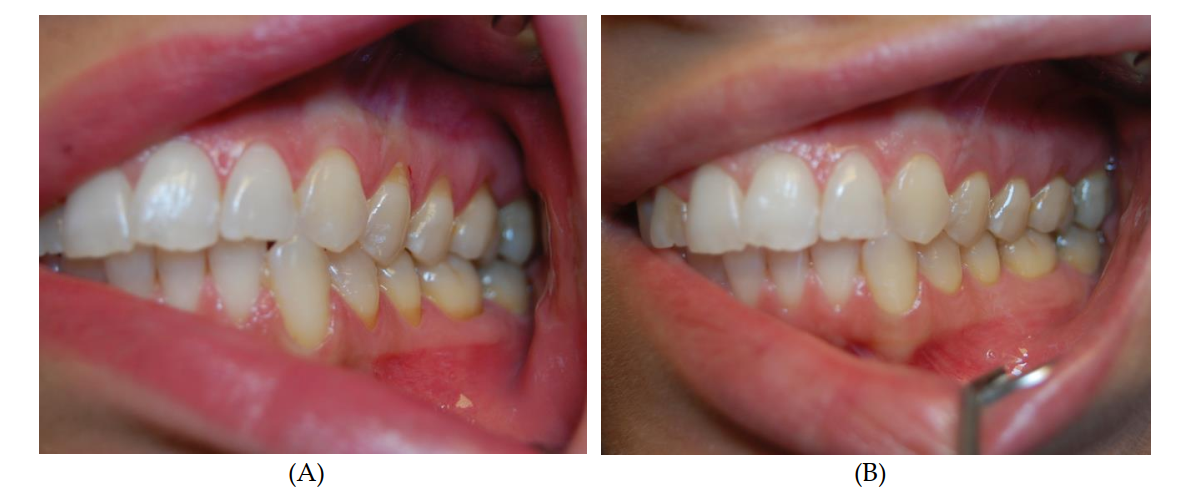
The aim of this study is the clinical observation of gingival tissue condition after atelocollagen injection. Methods: In 18 patients, 97 gingival class I Miller recessions were divided according to recession height, gingival papillae loss and thickness of gingivae. Atelocollagen (Linerase, 100 mg) was injected into keratinized gingivae twice or thrice, at two-week intervals.
Results: Statistically significant changes in gingival recession, amount of gingival papillae loss and thickness of gingiva were observed, after both two and three collagen injections. Although the degree (height) of recession decreased and gingival tissue thickness increased with every injection; there was no difference in gingival papillae loss between second and third collagen injections. Conclusions: The injectable form of atelocollagen is a promising material for gingival soft tissue regeneration and stimulation and allows for reduction in the number of procedures and support in a variety of surgical scenarios. This is a pilot study that clinically measures the impact of injected atelocollagen on periodontal tissue biotype, including the thickness of gingivae and gingival papillae regeneration.
Due to the significant deficiency of collagen found in aging skin, the use of collagen as a biostimulant has, therefore, been highly desirable. The interest in collagen increased greatly after the ability to synthetize its human form. In dentistry, the loss of tissues supporting teeth is a major problem, with a considerable impact on quality of life and aesthetic appearance. Gingival recessions, as the result of dental plaque accumulation, aggressive tooth brushing, periodontal diseases and orthodontic treatment, are large-scale for the population’s problem [1].
Gingival connective tissue consists predominantly of fibroblasts (5%), as well as other cells, such as mast cells, macrophages, neutrophilic granulocytes, lymphocytes and plasma cells, present in the lamina propria of oral mucosa. The extracellular matrix contains glycosaminoglicans, such as hyaluronic acid, dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate, proteoglycans, glycoproteins and fibers, such as reticulin fibers, collagen fibers, oxytalan and elastic fibers. Collagen fibers (65% of volume) play a key role in the gingival architecture of healthy gingiva, as well as in periodontal disease progression [2]. The level of collagen loss is highlighted as the main marker of this process [3].

Xem thêm